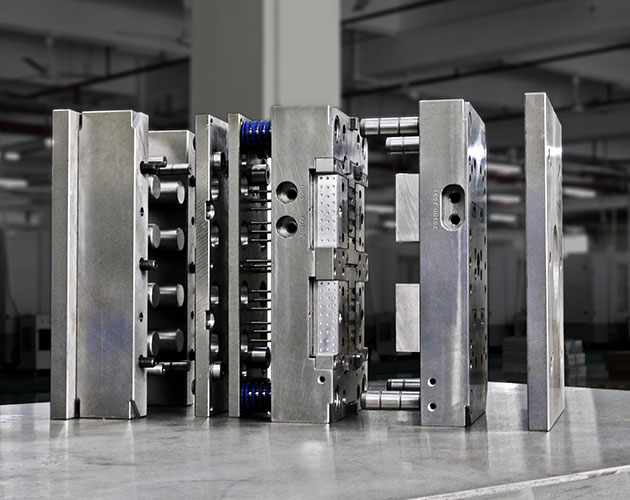
Precision mold
The thermoplastic injection molding process is a standard process that involves an aluminum mold and no heating or cooling lines pass through it, which means a longer cycle time. It allows our molds to monitor the filling pressure, appearance issues, and the basic quality of the parts.
The resin particles are put into a bucket, where they will eventually be melted, compressed, and injected into the runner system of the mold. The hot resin is injected into the mold cavity through the gate to form the part. The ejector pin facilitates the removal of the part from the mold, where the part falls into the loading bin. When the run is complete, the part (or initial sample run) will be boxed and delivered soon.
The following are its biggest advantages:
High efficiency
The mold injection process is of highly efficience for small-batch prototyping service with the quantity of 500~5000PCS.
Excellent details
High-pressure injection ensures that the molten material reaches every gap in the mold before it solidifies. This allows design engineers to incorporate complex geometries and complex elements into their designs.
Cost-effective
Fast and efficient production ensures low cost of each part, while high production yields further economies of scale. Aluminum is a cost-effective, readily available material that can be used as a cost control tool.
Mass production
The use of steel molds for injection molding can facilitate the mass production of millions of parts.
High tensile strength
Adding fillers to the liquid resin can enhance the tensile strength of injection molded parts.
rapid prototyping
Through proper treatment, the injection molded parts have a smooth finish when they come out of the mold, and no further refinement is required.
Material selection of injection molding
Below is a list of our standard materials that can be used for injection molding. If you need customized information, please contact us.
Acetal polyoxymethylene (POM)

ABS polycarbonate (PC-ABS)

Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS)

Polyethylene terephthalate (PET)

Nylon 66 (PA66)

Polymethyl methacrylate (acrylic) (PMMA)

Glass-filled, polyamide (PA-GF)

Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS)

High-density polyethylene (HDPE)

Polypropylene (PP)

Low-density polyethylene (LDPE)

Polystyrene (PS)

Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT)

Polystyrene + polyphenyl ethers (PS-PPE)

Polycarbonate (PC)

Thermoplastic elastomer (TPE)

Glass-filled polycarbonate (PC-GF)

Thermoplastic vulcanizates (TPV)

Automobile industry
Toy
Plastic hand board
Medical health
Electronic product
Aerospace
Smart home
Concept products
Home appliances